The L-11 76.2 mm tank gun was a [Soviet] 
(Soviet Union - Wikipedia) tank gun, used on the earliest models of the T-34 Model 1940 medium tank and KV-1 Model 1939 heavy tank during World War II.
 The 76 mm tank gun M1940 F-34 (76-мм танковая пушка обр. 1940 г. Ф-34 ) was a 76.2 mm Soviet tank gun used on the T-34/76 tank. A modified version of the gun, the 76 mm tank gun M1941 ZiS-5 (76-мм танковая пушка обр. 1941 г. ЗиС-5 ), was used on KV-1 tanks during World War II.
The 76 mm tank gun M1940 F-34 (76-мм танковая пушка обр. 1940 г. Ф-34 ) was a 76.2 mm Soviet tank gun used on the T-34/76 tank. A modified version of the gun, the 76 mm tank gun M1941 ZiS-5 (76-мм танковая пушка обр. 1941 г. ЗиС-5 ), was used on KV-1 tanks during World War II.
 .
.
There was a 57 mm gun considered for the KV-1, but AFAIK it was just a proposal and never fully developed, let alone built.
The tank in the photo is not armed with a 57 mm gun. It is armed with the ZIS-5 76 mm gun. However, the ZIS-5 tested in early 1941 and the ZIS-5 put into production in August were different guns. This gun had the ballistics of the 76 mm model 1931 AA gun. It passed trials, but production of barrels was complicated, so the gun went into production with the F-34 barrel, giving it identical ballistics to the T-34’s gun. More details in this article: http://www.tankarchives.ca/2017/07/big-gun-for-small-turret.htmlIt’s not a 57mm ZiS-4, it’s a 76mm L/51 F-27 gun (based on 76mm 3-K aa gun probably). Later it was chopped down to L/41 length (ZiS-5 gun)  . The T-44 was a medium tank developed and produced near the end of World War II by the Soviet Union. It was the successor to the T-34, offering an improved ride and cross-country performance, along with much greater armor. Designed to be equipped with an 85 mm main gun, by the time it was fully tested the T-34 had also moved to this weapon. Both tanks offered similar performance, so introducing the T-44 was not considered as important as increasing T-34 production. Fewer than 2,000 T-44s were built, compared to about 58,000 T-34s. Although the T-44 was available by the end of the war, it was not used in any battle. It was 1 ton lighter than the T-34-85 and slightly faster. The T-44 was heavily influential on the design of the T-54/55 Medium tank, most prominently lower hull and turret profiles. Also notable was the T-44-100, a 100mm D-10T-armed prototype, which would be the same 100mm gun mounted on the T-54/55, bar some minor changes.
. The T-44 was a medium tank developed and produced near the end of World War II by the Soviet Union. It was the successor to the T-34, offering an improved ride and cross-country performance, along with much greater armor. Designed to be equipped with an 85 mm main gun, by the time it was fully tested the T-34 had also moved to this weapon. Both tanks offered similar performance, so introducing the T-44 was not considered as important as increasing T-34 production. Fewer than 2,000 T-44s were built, compared to about 58,000 T-34s. Although the T-44 was available by the end of the war, it was not used in any battle. It was 1 ton lighter than the T-34-85 and slightly faster. The T-44 was heavily influential on the design of the T-54/55 Medium tank, most prominently lower hull and turret profiles. Also notable was the T-44-100, a 100mm D-10T-armed prototype, which would be the same 100mm gun mounted on the T-54/55, bar some minor changes.

 KV-1S
KV-1S KV-85
KV-85 .
.  KV-1E
KV-1E





 .
.  . KV-220-2. 85 mm F-30 cannon
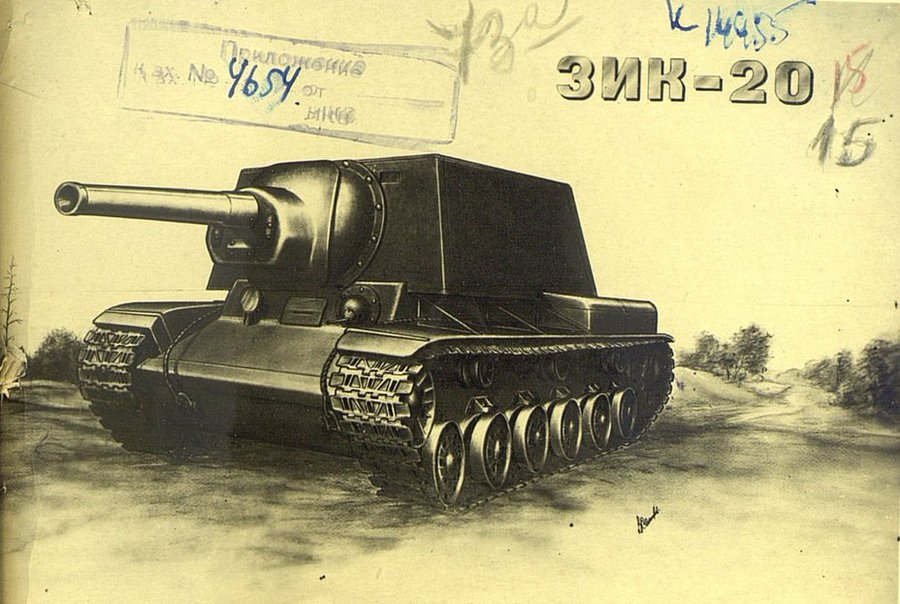
. KV-220-2. 85 mm F-30 cannon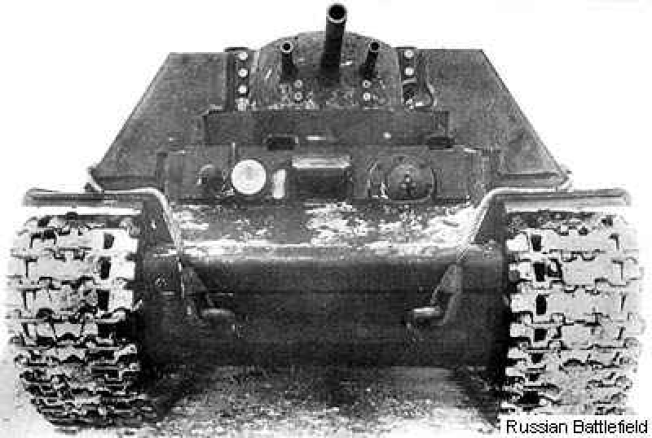  * KV-7-2 (improved variant) (also called U-14) had two 76 mm F-34 cannons, and 85 mm of frontal armour. Vehicles were not taken in service primarily because they could not fight tanks (the KV-7s had only 15-degree gun traverse to each side) and could not combat concrete bunkers due to the small caliber of the guns. After the failure of the KV-7 it was decided to put one 152 mm gun in the casemate instead of three smaller guns; this led to the development of the
* KV-7-2 (improved variant) (also called U-14) had two 76 mm F-34 cannons, and 85 mm of frontal armour. Vehicles were not taken in service primarily because they could not fight tanks (the KV-7s had only 15-degree gun traverse to each side) and could not combat concrete bunkers due to the small caliber of the guns. After the failure of the KV-7 it was decided to put one 152 mm gun in the casemate instead of three smaller guns; this led to the development of the  kv9. KV-10 (Object 230) - Also known as KV-1K. A KV-1 with 4 rocket launchers on the sides of its hull. Each launcher contained two 132 mm
kv9. KV-10 (Object 230) - Also known as KV-1K. A KV-1 with 4 rocket launchers on the sides of its hull. Each launcher contained two 132 mm